Understanding Nursing Home Costs and Options
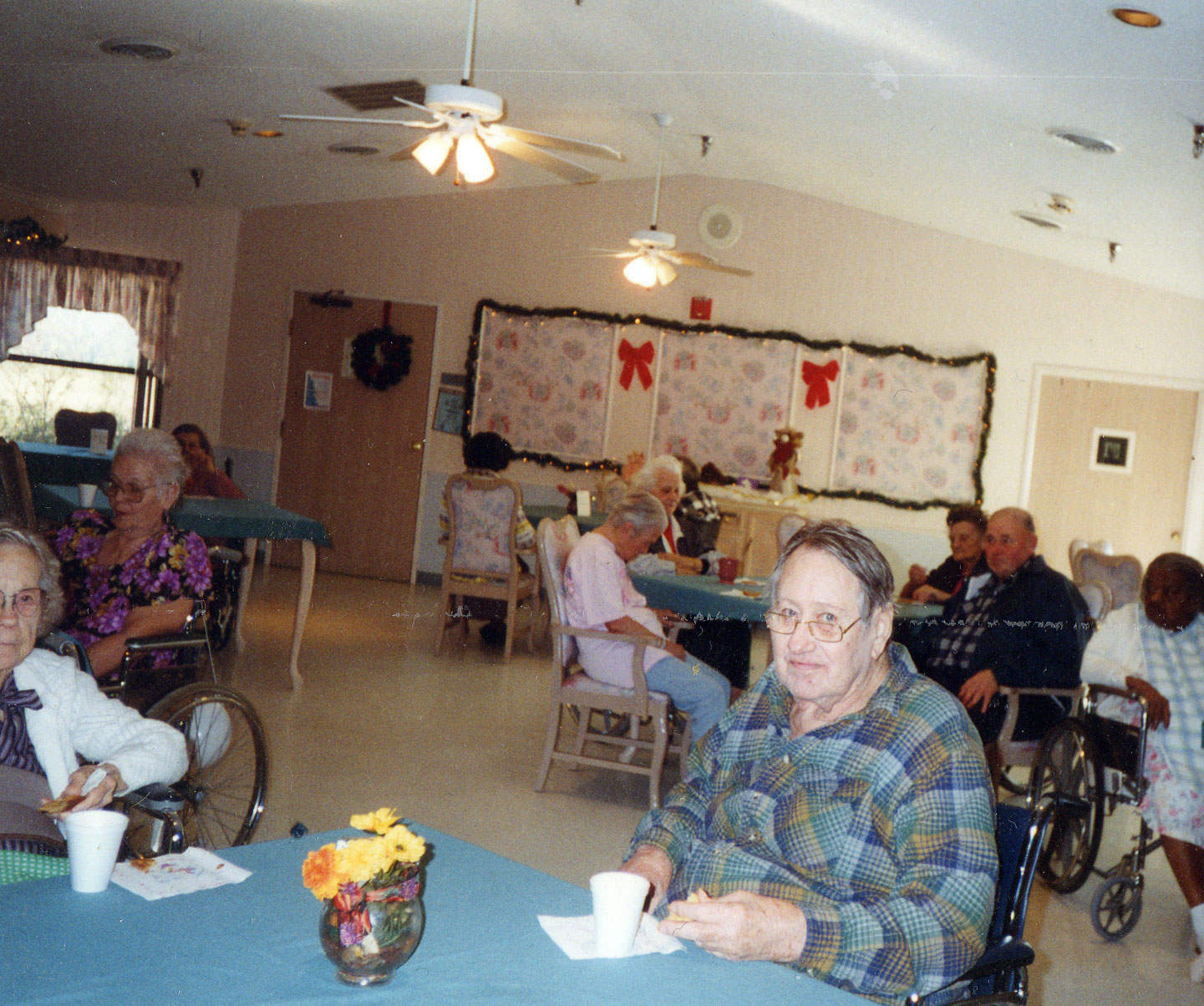
Navigating the landscape of long-term care often becomes a pivotal and challenging moment for families dealing with the health needs of their elderly, disabled, or ill loved ones. The focal point of this challenge often revolves around nursing homes, known for their comprehensive care but also synonymous with significant financial burdens. Before committing to a nursing home, families are encouraged to explore the diverse spectrum of care alternatives available, such as assisted living arrangements and in-home care solutions. This exploration phase is critical as it helps in comprehensively understanding the nuances in services offered, as well as the associated costs, thereby empowering families to make well-informed decisions regarding their loved one’s long-term care journey.
The decision-making process regarding long-term care is multifaceted, requiring careful consideration of various factors. Assisted living facilities, for instance, provide a balanced mix of independence and necessary assistance tailored to individual needs. In-home care, on the other hand, offers personalized support in the familiar comfort of one’s residence. Comparing these options against the comprehensive medical services and round-the-clock care provided in nursing homes becomes imperative to ensure the chosen path aligns with the specific requirements and financial capabilities of the family.
Delving into these choices isn’t merely about discerning the services on offer; it’s equally about understanding the financial implications. Nursing homes, while offering extensive medical care, often come with a higher price tag. Understanding the costs involved, including the average expenses for different types of rooms and any additional services required, aids families in preparing financially for the long-term care journey.
Moreover, this exploration phase isn’t solely about financial preparedness; it’s about ensuring the best possible quality of life for the individual needing care. By understanding the distinct services offered across various care options and their associated costs, families can tailor their decisions to meet the specific medical and emotional needs of their loved ones, promoting a sense of security and well-being throughout their long-term care experience.
Ultimately, exploring the diverse landscape of long-term care options isn’t a one-size-fits-all endeavor. It’s a tailored journey unique to each family’s circumstances and the needs of their loved ones. Through this exploration, families can navigate the intricate web of services and costs, making informed choices that ensure both the financial stability and the well-being of their cherished family members in need of long-term care.
Nursing Home Costs Explained
Nursing homes stand as stalwart pillars in the realm of long-term care, distinguished by their unwavering commitment to providing intensive round-the-clock skilled nursing care, coupled with indispensable assistance in daily living activities. This comprehensive care serves as a cornerstone in catering to individuals with intricate medical needs, setting nursing homes apart from other long-term care options like assisted living facilities.
Unraveling the financial dimensions of nursing home care sheds light on the significant investment families must consider. The Genworth Financial Cost of Care Survey in 2020 underscored the substantial expense families encounter, with the average monthly cost for a semi-private room hovering around $7,756. However, these figures aren’t universal, as costs can significantly vary based on geographical location, rendering it essential for families to factor in regional disparities when planning for long-term care.
Moreover, the duration of stay within nursing homes extends beyond short-term rehabilitation, often averaging approximately 485 days. This extended duration inherently contributes to the cumulative financial implications, necessitating families to prepare for a longer-term financial commitment. Additionally, these costs represent the baseline expenses, with specialized services and medical requirements accruing additional charges, further augmenting the financial burden borne by families.
While these figures might seem daunting, it’s crucial to recognize that the investment in nursing home care encompasses not just monetary considerations but also addresses the critical need for specialized medical attention and round-the-clock support. The costs incurred are reflective of the comprehensive care and specialized services tailored to meet the complex needs of individuals requiring long-term care. This level of care goes beyond mere assistance, providing a nurturing environment that fosters health, well-being, and a sense of security for residents.
Understanding the financial aspect of nursing home care isn’t just about acknowledging the expenses; it’s about appreciating the value and significance of the services rendered. Families navigating this financial landscape are not merely investing in a facility; they are entrusting the well-being and quality of life of their loved ones into the hands of dedicated professionals committed to providing unparalleled care and support throughout their stay.
Private Pay and Financial Options
Navigating the labyrinth of financing options for nursing home care requires a comprehensive understanding of the diverse avenues available to families seeking financial assistance. While nursing home costs might seem daunting, various strategies can help alleviate the financial burden, offering families an array of choices to explore.
Home Health Services emerge as an initial consideration for some families, offering partial coverage by Medicare, particularly for short-term rehabilitative care. This avenue provides a valuable lifeline, offering up to 35 hours per week of in-home assistance, including skilled nursing care and, to some extent, light housekeeping duties. This option not only supports the well-being of the individual in need but also allows them to remain in the comfort of their own home, fostering a sense of familiarity and security.
However, for more substantial or extended nursing home care needs, families often delve into more substantial financial strategies. Tapping into home equity through reverse mortgages stands as one such option, utilizing the accumulated equity in the home to defray the costs of nursing home care. While this strategy offers immediate financial relief, it’s imperative to carefully scrutinize the terms and implications of a reverse mortgage, as it involves obligations and potential repercussions.
Additionally, individuals might consider leveraging their retirement savings accounts, such as a 401(k) or IRA, to cover nursing home expenses. Nevertheless, liquidating these accounts necessitates a cautious approach due to potential tax implications and financial repercussions. Seeking guidance from financial advisors or tax professionals becomes imperative in navigating these waters, ensuring informed decisions that mitigate adverse financial consequences.
Understanding the implications of these financial options transcends mere monetary considerations. Each strategy carries its own set of intricacies, intertwining financial implications with potential tax ramifications and long-term repercussions. Families navigating these decisions must weigh not only the immediate financial relief but also the long-term financial security and well-being of their loved ones in need of care.
Ultimately, the pursuit of financial options for nursing home care isn’t just about mitigating costs; it’s about ensuring the best possible quality of care while maintaining financial stability. Each option represents a pathway toward providing comprehensive care and support, but it’s the informed decisions guided by financial expertise that pave the way for a more secure and sustainable long-term care journey.
Long-Term Care Insurance: A Viable Solution
Long-term care insurance emerges as a proactive and strategic financial tool designed to address the substantial expenses associated with nursing home care. This insurance serves as a protective shield, offering financial coverage for long-term care needs, provided individuals have secured the policy well in advance. The efficacy of this insurance hinges upon its longevity, emphasizing the significance of early planning and acquisition.
The evolution of long-term care insurance has seen newer policies integrated with permanent life insurance, presenting policyholders with more dynamic and flexible options. These innovative policies, often known as hybrid or linked policies, not only safeguard against potential long-term care expenses but also offer access to the policy’s value to cover these costs. This dual-purpose approach resonates with individuals seeking both security in their long-term care needs and financial value within a single insurance plan.
However, the efficacy and relevance of long-term care insurance policies pivot on the thorough understanding of their terms, conditions, and coverage specifics. Each policy exhibits unique features and nuances, necessitating a meticulous examination to ensure alignment with an individual’s specific care needs and financial circumstances. Factors such as waiting periods, coverage limitations, and benefit triggers demand careful scrutiny to ascertain the policy’s suitability and utility.
Furthermore, the decision to invest in long-term care insurance isn’t solely about acquiring a policy; it’s about ensuring its functionality and relevance over time. As individuals progress through life stages, their care needs and financial situations evolve, highlighting the importance of periodic reassessment and potential policy adjustments to accommodate changing circumstances effectively.
The efficacy and viability of long-term care insurance materialize when individuals make informed decisions, driven by a comprehensive understanding of the policy’s intricacies and its capacity to address long-term care expenses. It serves as a proactive financial safeguard, offering not just coverage against potential nursing home expenses but also a sense of assurance and preparedness in navigating the uncertainties of future care needs.
Ultimately, the pursuit of long-term care insurance isn’t just about acquiring a policy; it’s about securing peace of mind and financial stability. When individuals align their long-term care insurance choices with their evolving needs and financial objectives, it becomes a cornerstone in their strategy to ensure comprehensive and sustainable long-term care solutions.
Medicare and Medicaid Assistance
Medicare typically covers the initial 100 days of a nursing home stay for intensive rehabilitation purposes but doesn’t cater to long-term stays unless supplemented by a Medicare Advantage policy with nursing home coverage. Medicaid often becomes the last resort for funding nursing home care, involving stringent means testing of income and assets to qualify for coverage.
Medicare and Medicaid serve as pivotal pillars in the landscape of healthcare coverage, particularly in addressing the needs of individuals requiring long-term nursing home care. Understanding the roles and limitations of these programs becomes imperative for families navigating the complex terrain of financing.
Medicare, the federally funded health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, offers coverage for the initial 100 days of a nursing home stay, specifically designed for intensive rehabilitative care following an injury or illness. However, Medicare doesn’t extend its coverage to long-term stays unless supplemented by a Medicare Advantage policy, also known as Part C, encompassing specialized nursing home coverage. This supplemental policy extends beyond the basic Medicare coverage, providing additional benefits tailored to individual needs, including nursing home care. It’s essential for individuals contemplating Medicare Advantage policies to thoroughly assess and ensure that the selected policy aligns with their long-term care needs.
In contrast, Medicaid often emerges as the last resort for funding nursing home care, particularly for those with limited financial resources. However, qualifying for Medicaid involves stringent means testing, scrutinizing both income and asset levels. Medicaid sets stringent income thresholds, usually not exceeding a certain monthly income limit, and assesses assets, often allowing minimal assets, such as $2,000, for an individual to qualify for coverage. This means testing is aimed at ensuring coverage for those with limited financial means, rendering Medicaid a safety net for those unable to afford private payment or lacking comprehensive insurance coverage for nursing home care.
Navigating the realm of Medicare and Medicaid involves comprehending not just the coverage provided but also the eligibility criteria and potential limitations associated with these programs. While Medicare caters to short-term rehabilitative care, individuals seeking long-term care must explore supplemental policies. Conversely, Medicaid serves as a safety net, catering to those with limited financial resources but involves strict eligibility criteria that necessitate careful planning and assessment.
Understanding the interplay between Medicare, Medicaid, and individual long-term care needs is crucial for families aiming to navigate the complexities of financing nursing home care. It’s through this comprehensive understanding that families can make informed decisions, ensuring the best possible care while maintaining financial stability for their loved ones in need of long-term care.
The Bottom Line: Balancing Costs and Care
The affordability of long-term care remains a pressing issue in the United States. Finding a balance between private pay and government programs is often necessary. Consulting financial advisors and leveraging tools like SmartAsset’s advisor matching tool or Retirement Tax Calculator can provide valuable guidance in navigating long-term care planning and financial considerations.
The intersection of cost and care in the realm of long-term care presents a formidable challenge for families across the United States. Balancing the financial aspects with the imperative need for comprehensive care stands as a pivotal consideration in ensuring the well-being of loved ones requiring long-term care.
Affordability remains a poignant concern, underscoring the need to explore a balanced approach that incorporates both private payment options and government programs. This equilibrium involves a meticulous evaluation of available financial resources, potential insurance coverage, and eligibility for government aid programs like Medicare and Medicaid. Striking this balance necessitates a holistic understanding of individual financial capacities and the intricate web of available support systems.
Engaging financial advisors emerges as a strategic step in this balancing act, offering expertise and insights to navigate the intricate landscape of long-term care planning. These professionals provide valuable guidance, leveraging their knowledge to craft tailored financial strategies that align with individual needs and resources. Utilizing tools such as SmartAsset’s advisor matching tool or Retirement Tax Calculator further augments this approach, empowering individuals with comprehensive financial insights and aiding in decision-making.
Furthermore, these tools serve as beacons of knowledge, illuminating the intricate tax implications and financial intricacies associated with long-term care planning. They empower individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions, ensuring financial stability while prioritizing the well-being and quality of care for their loved ones.
The pursuit of this balance isn’t merely about mitigating costs; it’s about ensuring a sustainable and holistic approach to long-term care. It involves a delicate intertwining of financial prudence and compassionate caregiving, where decisions are not solely driven by monetary considerations but by a profound commitment to providing the best possible care and support.
In essence, finding this equilibrium between costs and care is a journey unique to each family, guided by their circumstances and the needs of their loved ones. It’s through informed decision-making, consultation with financial experts, and leveraging innovative tools that families can navigate this intricate balance, ensuring that long-term care remains both affordable and compassionate.
FAQs on Nursing Home Costs and Long-Term Care Options
1. What’s the difference between nursing homes and assisted living?
Nursing homes provide 24/7 skilled nursing care, while assisted living offers more independent living with some assistance. Nursing homes cater to those needing intensive medical care.
2. How much does a nursing home stay cost?
On average, a semi-private room in a nursing home costs around $7,756 per month, with variations based on location. Private rooms can be pricier, nearing $8,821 per month.
3. Can Medicare cover nursing home expenses?
Medicare typically covers the first 100 days for short-term rehabilitation, but not extended stays for long-term care unless supplemented by specific policies like Medicare Advantage.
4. What’s the role of Medicaid in nursing home payments?
Medicaid acts as a last-resort funding source for nursing home care, involving strict income and asset eligibility criteria to qualify for coverage.
5. How can long-term care insurance help with nursing home costs?
Long-term care insurance, when planned well in advance, can assist in covering expenses related to in-home care and residential facilities like nursing homes. However, policy terms vary, and understanding coverage is crucial.
6. Are there financial strategies to help with nursing home expenses?
Some people explore options like tapping into home equity through reverse mortgages or considering retirement accounts like 401(k) or IRAs. However, these decisions may have tax implications and should be approached with caution.
7. Can I rely on private pay for nursing home care?
Private pay, while an option, might not be sustainable for long-term care. It’s essential to consider a mix of private pay and potential government assistance programs.
8. What’s the average duration of a nursing home stay?
Statistics show an average nursing home stay lasting around 485 days, although this duration can vary based on individual needs and circumstances.
9. Is long-term care insurance suitable for everyone?
Long-term care insurance can be beneficial, but policies differ widely. Older policies might have limitations, and it’s crucial to ensure the policy aligns with your needs.
10. How can financial advisors assist in long-term care planning?
Financial advisors can provide guidance on navigating long-term care options, including choosing suitable insurance, understanding financial implications, and optimizing available resources.
Tags:
- Nursing home cost
- Long-term care options
- Financial strategies
- Medicare
- Medicaid
- Long-term care insurance
- Retirement planning
- Assisted living
- In-home care
- Financial advisors